Google makes over 4,500 changes to their algorithm every year.
So it’s fair to say that SEO changes fast.
Sure, many of the fundamentals of SEO (like optimizing your site’s on-page SEO and building backlinks) haven’t changed that much over the last few years.
But there are a handful of significant changes to SEO that are worth paying attention to. In fact, ignoring these important changes can hurt your site’s ability to rank in Google.
And in this post I’ll outline 5 SEO changes that might be keeping your site from Google’s first page.
1. Google’s Emphasis on Core Web Vitals
Google has been using page loading speed as part of their algorithm for years.
But in 2021, Google stepped things up with what they call “Core Web Vitals”.
Core Web Vitals are a set of three factors that Google considers important for UX.
In other words: this new set of ranking factors doesn’t look at the quality of your content. Or the number of backlinks you have.
Instead, Core Web Vitals are all about how users interact with your site.
Specifically, Core Web Vitals measure:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Essentially how long it takes for the majority of your page’s content to load.
First Input Delay (FID): How long it takes before a user can interact with your page (for example, entering their username).
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): How much a page shifts during the loading process (less is better).
It’s not yet known how much Core Web Vitals impact rankings. But they are a confirmed ranking signal. So if you haven’t been working to improve your Core Web Vitals, it’s likely that your rankings are suffering because of it.
To get a baseline of where you’re at, you can check out your Core Web Vitals scores in Search Console.

2. EAT Continues to Impact Health and Wellness Content
Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness (EAT) is Google’s way of sizing up how much a specific piece of content (or an entire site) can be trusted.
For example, a site can have well-written content. Great Core Web Vitals. And plenty of backlinks.
But that doesn’t necessarily mean that the content is completely accurate. Or written by someone with specific knowledge on the subject.
Which is why Google is relying more on signals that demonstrate high levels of EAT.
(Things like a site’s reputation, an author’s expertise, and transparency about any potential conflicts of interest).
While EAT likely applies to content about anything, Google likely puts much more emphasis on EAT for content about health.
For example, Healthline might be the #1 health site online (in terms of organic traffic).
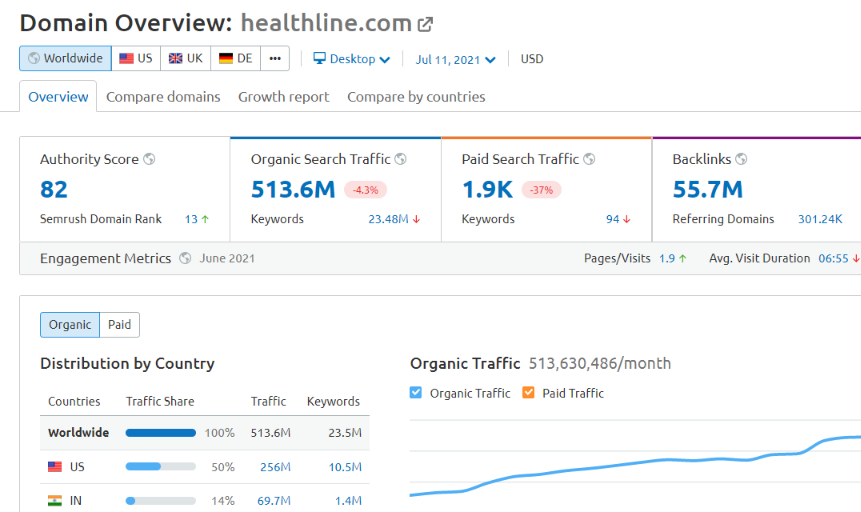
They’re able to rank for so many competitive keywords largely due to their focus on EAT.
Every article is written or reviewed by a healthcare professional. And each piece is referenced based on data from reputable medical journals.
3. Search Intent Becomes More Important
Google can easily measure how users interact with your site (assuming they land on your page from a Google search).
For example, let’s say a user clicks on the #1 result in Google. But they don’t find what they’re looking for. So they click “back” after 2 seconds.
That’s something Google can measure. And, if enough users have the same reaction to the top result, Google may demote that site lower down the page.
Which is why it’s super important that your page’s aren’t just keyword-optimized around a specific keyword. But that your page is optimized for what SEO professionals call “search intent”.
Search intent is essentially what a searcher wants from a given search. Sometimes they might want to get information on a topic. In other cases, a user may want to buy something.
And the more your content can align with that keyword’s search intent, the better you’ll tend to rank.
For example, we recently increased the organic traffic to the Exploding Topics blog by 37% simply by optimizing for search intent.
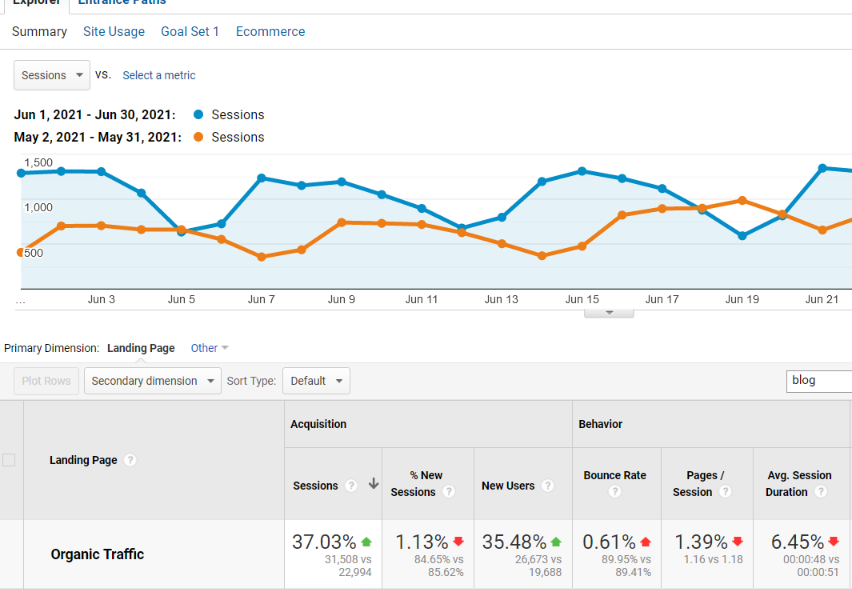
Specifically, we looked at the keyword that each page was trying to rank for. Hypothesized what specifically that searcher would want to see. And tweaked our content to better match search intent.
4. SERP Real Estate Becomes a Concern
Back in the day, you could basically estimate how much traffic you’d get from a keyword based on where you ranked.
So if you ranked #3 for a keyword with 1,000 searches per month, you could estimate that you’d get about 150 clicks per month.
It’s obviously better to rank higher up on Google’s first page. But things are far from that straightforward anymore.
That’s largely thanks to Google implementing dozens of new “SERP Features” over the past few years.
SERP features are essentially elements that Google adds to the results. Elements that aren’t a traditional “10 blue link” organic result.
For example, check out the search results for this keyword:
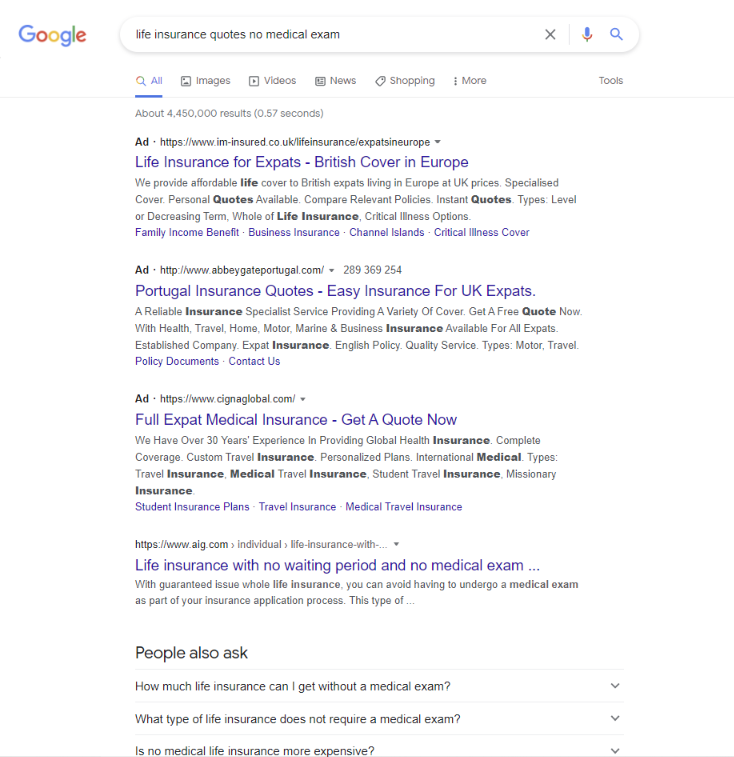
There are several prominent ads. A “People also ask” box. And more.
Which is why many SEOs are focusing more on SERP real estate over traditional ranking positions.
Specifically, they’re looking at where their site actually appears in the search results. And optimizing for increased visibility.
For example, they might try to rank their site in the top 3. And also have one of their YouTube videos or Medium articles rank on the first page as well.
Others will avoid keywords that have too many SERP features. The idea being that it’s not worth trying to rank “#1” for a keyword when you’ll actually be halfway down the page.
5. SEOs Push to Optimize for CTR
Whether click-through-rate is an organic ranking signal is up for debate.
Some SEOs (myself included) think that Google uses it to figure out whether or not a result is something searchers are even interested in clicking.
Others see CTR as a “noisy” signal that doesn’t factor into rankings.
But no matter where you stand on the issue, the fact remains that optimizing for CTR makes sense.
That’s because a higher CTR=more traffic. Even if your rankings don’t improve.
And, as outlined before, with organic clicks being eaten away by SERP features, improving your CTR is more important than ever before.
Fortunately, you don’t need to guess what pushes people to click on a specific result.
In general, pages with these attributes tend to have high CTRs:
Uses a number in the title tag
Has a unique description
Emphasizes content is new/recent
Uses terms that grab attention (without being too clickbaity)
Conclusion
That wraps up my list of 5 important SEO changes to keep an eye on.
All of these changes are currently impacting SEO. But it’s important to point out that they’re all likely to become more important as time goes on.
So if you want to get higher rankings today, but also improve your rankings over the long-term, it’s worth optimizing around these new changes.






